Describe How the Brain Changes With Continued Alcohol Use
When this happens the parts of the brain that regulate impulse control stress management and information processing can all be harmed. It went to their heads.
ALCOHOLS DAMAGING EFFECTS ON THE BRAIN.
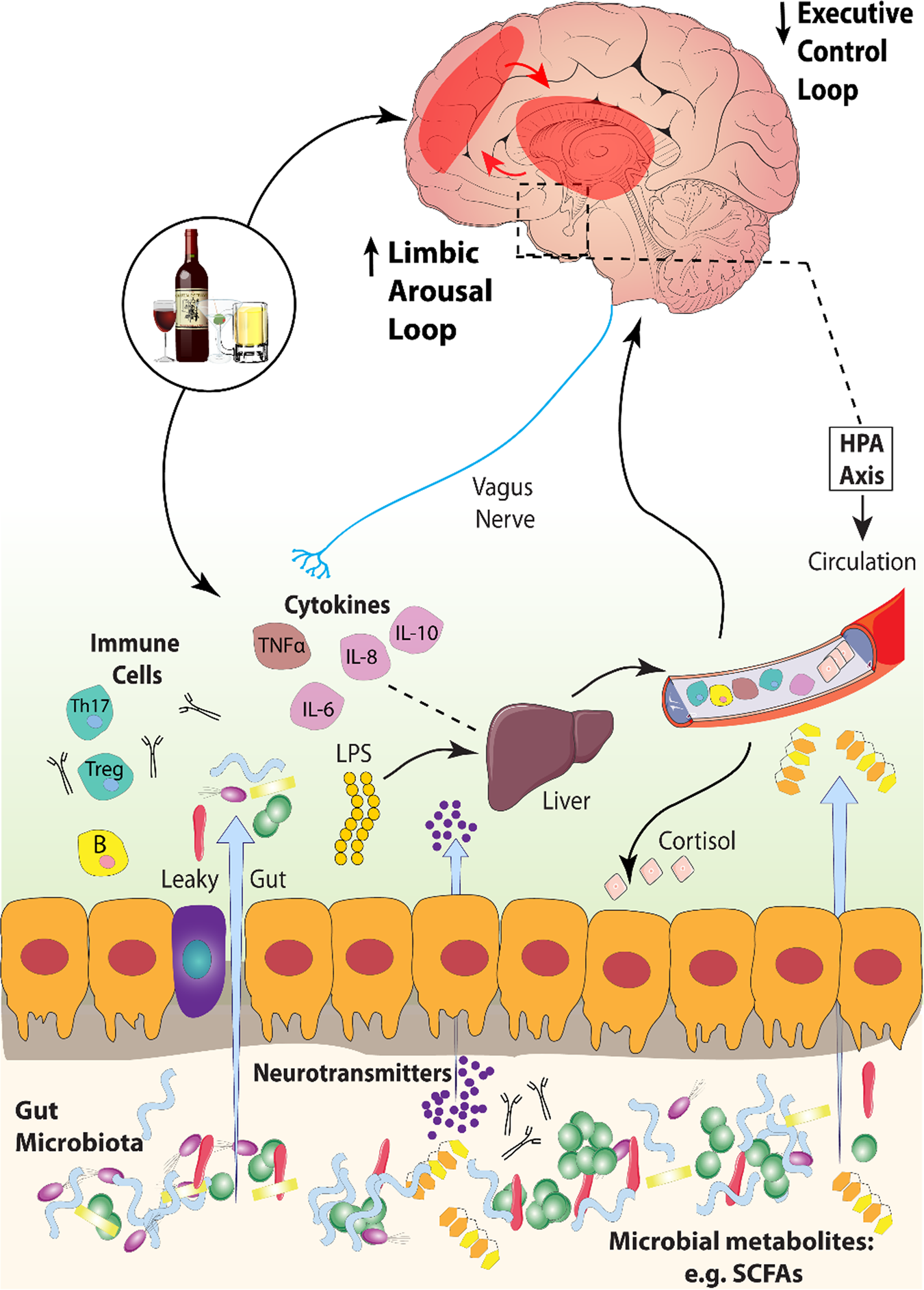
. Long-term heavy drinking causes alterations in the neurons such as reductions in their size. It can lead to Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome WKS which is marked by amnesia extreme confusion and eyesight issues. The result is transient or cognitive deficits from atrophy.
It may also cause our hands to shake. The MRI research revealed that alcohol abstinence led to brain volume increases in key areas including the frontal lobe and cerebellum. Alcohol impairs this brain region affecting our balance causing us to be unsteady stagger and possibly fall.
With long-term alcohol or drug abuse the brain physically changes. Alcohol abuse can increase your risk for some cancers as well as severe and potentially permanent brain damage. The first is neurotoxicity which occurs when.
The Cerebellum is the center of movement coordination equilibrium and balance. Some of these impairments are detectable after only one or. Alcohol makes it harder for the brain areas controlling balance memory speech and judgment to do their jobs resulting in a higher likelihood of injuries and other negative outcomes.
The finding provides a biological mechanism that helps to explain compulsive alcohol. This process of change is known as neuroplasticity. After alcohol leaves the system the brain continues over activating the neurotransmitters causing painful and potentially dangerous withdrawal symptoms that can damage brain cells.
When the researchers studied the positive changes in gray matter volume they concluded that. The sustained abuse of alcohol causes the brain to adapt and to almost rewire itself around the continuous presence of this chemical substance. Chronic alcohol exposure leads to brain adaptations that shift behavior control away from an area of the brain involved in complex decision-making and toward a region associated with habit formation according to a new study conducted in mice by scientists at the National Institutes of Health.
WKS is a brain disorder caused by a thiamine deficiency or lack of vitamin B-1. I always read anything about alcohol suspiciously because the stance on it changes regularly. Alcohol suppresses the release of glutamate causing the brains pathways to be slowed down tremendously.
The results of alcohol affecting the cerebral cortex are poor judgment and depressed inhibition which makes you more talkative and confident. One serious change that can result from repeated drinking is shrinkage of the brain. Experts associate excessive drinking with brain atrophy.
Alcohol affects this part of the brain and blunts your senses. Quickly the researchers say. Clearly alcohol affects the brain.
Stumbling and poor balance Alcohol can damage your cerebellum which could cause permanent changes in your coordination and sense of balance. 14 Alcohols damage to the brain can take several forms. The developing brain is particularly vulnerable to effects of alcohol.
In addition to this alcoholism damages portions of the hypothalamus by breaking blood vessels in this area of the brain. The researchers conducted multiple scans to track the changing state of the brain over time. This neurotransmitter is responsible for energy levels and brain activity.
Brain Atrophy The neurotoxic effects of alcohol on the brain cause the white matter and cerebral cortex to shrink. Alcohol stimulates the release of dopamine which is why it has a strong addictive nature. The result of these changes is that alcoholics become less able to make good decisions and to practice self-control.
Acetaldehyde for instance is a known carcinogen so I dont understand how a substance that causes cancer and shrinks the brain can also be recommended in moderation. Essentially the overflow causes mild sedation of the brain. Two crucial parts of the brain that control memory learning decision-making and personality are especially vulnerable to alcohol as a child grows.
With the continued use of alcohol chronic changes can develop over time. Dopamine the brains third chemical messenger serves as the brains pleasure center. Only 6 minutes after consuming an amount of alcohol equivalent to three beers leading to a.
Excessive alcohol intake binge drinking causes a decrease in hippocampal neurogenesis via decreases in neural stem cell proliferation and newborn cell survival. If you drink a lot of alcohol there can even be permanent changes to the structure of your brain. Difficulty walking blurred vision slurred speech slowed reaction times impaired memory.
Perhaps one of the most alarming long-term effects of alcohol use on the brain is the potential development of physiological dependence a state and condition in which a person experiences physical and psychological withdrawal symptoms and cravings if they cease drinking or significantly lower the amount of alcohol in their body. The ability to stop drinking is severely. Brains of alcoholics resemble brains of chronologically old nonalcoholics.
Poor memory Alcohol can keep the chemicals in your brain from working. This can lead to a variety of effects including. This involved both gray matter and white matter.
Brains of alcoholics resemble brains of chronologically old nonalcoholics. Alcohol decreases the number of cells in S-phase of the cell cycle and may arrest cells in the G1 phase thus inhibiting their proliferation. It also increases your threshold for pain while affecting thought processes in the cerebral cortex.
This happens every time alcohol is consumed a GABA increase and will happen more and more intensely over time as long as there is drinking. Long-term use of alcohol can permanently damage the cerebral cortex. This may occur at the onset of problem drinking accelerated aging or later in life when brains are more vulnerable increased vulnerability or cumulative effects.
The shrinkage is probably due to a loss of neurons grey matter and glial cells white matter the other major type of cell in the brain. In response to increased GABA levels the brain creates more glutamate an excitatory neurotransmitter. GABA does the opposite of.
123 This damage is made worse by drinking binges and sudden withdrawal. At the end of the day however alcohol is a recognized toxin as are its byproducts. Alcohol can cut short its healthy growth and re-wire it in ways that cause physical emotional and social harm to a child1.
Memory and learning are controlled by a part of the brain called. This may occur at the onset of problem drinking accelerated aging or later in life when brains are more vulnerable increased vulnerability or cumulative effects. The brain actually shrinks and its ability to process information is damaged.
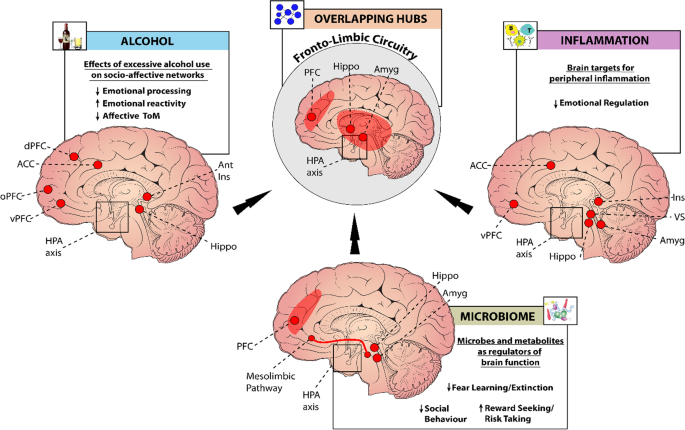
A Biological Framework For Emotional Dysregulation In Alcohol Misuse From Gut To Brain Molecular Psychiatry

A Biological Framework For Emotional Dysregulation In Alcohol Misuse From Gut To Brain Molecular Psychiatry
Content Repeated Use Of Alcohol Can Cause Long Term Changes In The Brain The Alcohol Pharmacology Education Partnership


No comments for "Describe How the Brain Changes With Continued Alcohol Use"
Post a Comment